This Guide * عن هذا الدليل
The purpose of this guide is to help students and researchers at all levels to learn and explore topics related to Arabic literature  of various periods. The guide serves as a starting point and an introduction to resources available through Cornell University Library system and beyond. Some of the content is only accessible to students, faculty, and staff of Cornell University. The guide aims to provide links to selected sources, which offer diverse, objective, balanced and rational perspectives of the topics. Your first point of contact with these resources should be the library discovery tool (online catalog). This is where you will find information on all types of materials and how to get them. You will also find information on your loans, opening hours, and subject specialists who can answer your questions.
of various periods. The guide serves as a starting point and an introduction to resources available through Cornell University Library system and beyond. Some of the content is only accessible to students, faculty, and staff of Cornell University. The guide aims to provide links to selected sources, which offer diverse, objective, balanced and rational perspectives of the topics. Your first point of contact with these resources should be the library discovery tool (online catalog). This is where you will find information on all types of materials and how to get them. You will also find information on your loans, opening hours, and subject specialists who can answer your questions.
![]() Disclaimer of Endorsement: The University does not necessarily agree with assertions and opinions expressed in the resources listed in this guide. These are provided for the researcher to discover, contrast and compare.
Disclaimer of Endorsement: The University does not necessarily agree with assertions and opinions expressed in the resources listed in this guide. These are provided for the researcher to discover, contrast and compare.![]()
الغرض من هذا الدليل هو مساعدة الطلاب والباحثين على جميع المستويات على تعلم واستكشاف الموضوعات المتعلقة بالأدب العربي لجميع الفترات. يخدم الدليل كمقدمة للموارد المتاحة من خلال نظام مكتبة جامعة كورنيل. بعض المحتوى متاح فقط للطلاب وأعضاء هيئة التدريس وموظفي جامعة كورنيل. يهدف هذا الدليل إلى توفير روابط لمصادر مختارة، والتي تقدم وجهات نظر متنوعة وموضوعية ومتوازنة وعقلانية للمواضيع. يجب أن تكون نقطة الاتصال الأولى مع هذه الموارد هي أداة اكتشاف المكتبة (كتالوج عبر الإنترنت). هذا هو المكان الذي ستجد فيه معلومات عن جميع أنواع المواد وكيفية الحصول عليها. سوف تجد أيضا معلومات عن القروض الخاصة بك ، وساعات العمل ، والمتخصصين الذين يمكنهم الإجابة عن أسئلتك.
![]() تنويه: إخلاء مسؤولية عن الإقرار: لا توافق الجامعة بالضرورة على التأكيدات والآراء الواردة في الموارد المذكورة في هذا الدليل. يتم توفير هذه للباحث للاكتشاف والمقارنة.
تنويه: إخلاء مسؤولية عن الإقرار: لا توافق الجامعة بالضرورة على التأكيدات والآراء الواردة في الموارد المذكورة في هذا الدليل. يتم توفير هذه للباحث للاكتشاف والمقارنة.![]()
Quick Browse * The Online Catalog
Search/Browse
Quick Links: Online Catalog & Databases
The following list uses subject 'tags' from bibliographic records in Cornell's Online Catalog![]() to pull up lists of titles on specific subjects in the collections. Click on one of the subject headings to see a list of relevant titles:
to pull up lists of titles on specific subjects in the collections. Click on one of the subject headings to see a list of relevant titles:
Narrower Term:
- Arab American literature
- Arabic drama
- Arabic essays
- Arabic fiction
- Arabic letters
- Arabic poetry
- Arabic prose literature
- Arabic wit and humor
- Christian literature, Arabic
- Dialect literature, Arabic
- Epic literature, Arabic
- Exiles' writings, Arabic
- Folk literature, Arabic
- Gay men's writings, Arabic
- Hypertext literature, Arabic
- Immigrants' writings, Arabic
- Islamic literature, Arabic
- Ismaili literature
- Physicians' writings, Arabic
- Prisoners' writings, Arabic
- Qurʾan as literature
- Revolutionary literature, Arabic
- Shiite literature
- Shiite literature, Arabic
- Sufi literature
- Travelers' writings, Arabic
 Try these call number ranges for specific searches in the Online Catalog or the stacks [Call numbers in the 'Library of Congress Classification']:
Try these call number ranges for specific searches in the Online Catalog or the stacks [Call numbers in the 'Library of Congress Classification']:
- PJ6001-8517
 Arabic Language
Arabic Language
- PJ6690-6697
 Ancient Arabic
Ancient Arabic
- PJ6701-6901
 Modern Arabic dialects
Modern Arabic dialects
- PJ6950-7144
 South Arabian
South Arabian
- PJ6950-6981
 Ancient South Arabian
Ancient South Arabian
- PJ7051-7144
 Modern South Arabian
Modern South Arabian
- PJ7501-8517
 Arabic literature
Arabic literature
- PJ7695.8-7796
 Individual authors or work
Individual authors or work
Background * Introduction * تقديم: أدب
Arabic literature
Arabic literature is the body of works produced in the Arabic language, both prose and poetry. The Arabic word used for literature is "Adab = أدب," which is derived from a meaning of etiquette, and which implies politeness, culture and enrichment. The tradition of Arabic literature stretches back to unrecorded beginnings in the Arabian Peninsula, but with only fragments of the written language appearing before the 5th century. It does not usually include works written using the Arabic alphabet but not in the Arabic language such as Persian literature and Urdu literature. The Qur'an, widely regarded as the finest piece of literature in the Arabic language, would have the greatest lasting effect on Arabic culture and its literature.

الأدب العربي
الأدب العربي يشمل الأعمال المكتوبة باللغة العربية، من نثر و شعر وكذلك يشمل الأدب القصصي والرواية والمسرح والنقد. تمتد أصول الأدب العربي إلى بدايات غير مسجلة في شبه الجزيرة العربية، ولكن مع أجزاء من اللغة المكتوبة فقط تظهر قبل القرن الخامس الميلادي. يعتبر القرآن على نطاق واسع أرقى جزء من الأدب في اللغة العربية، وهو الأثر الدائم الأكبر على الثقافة العربية وأدبها
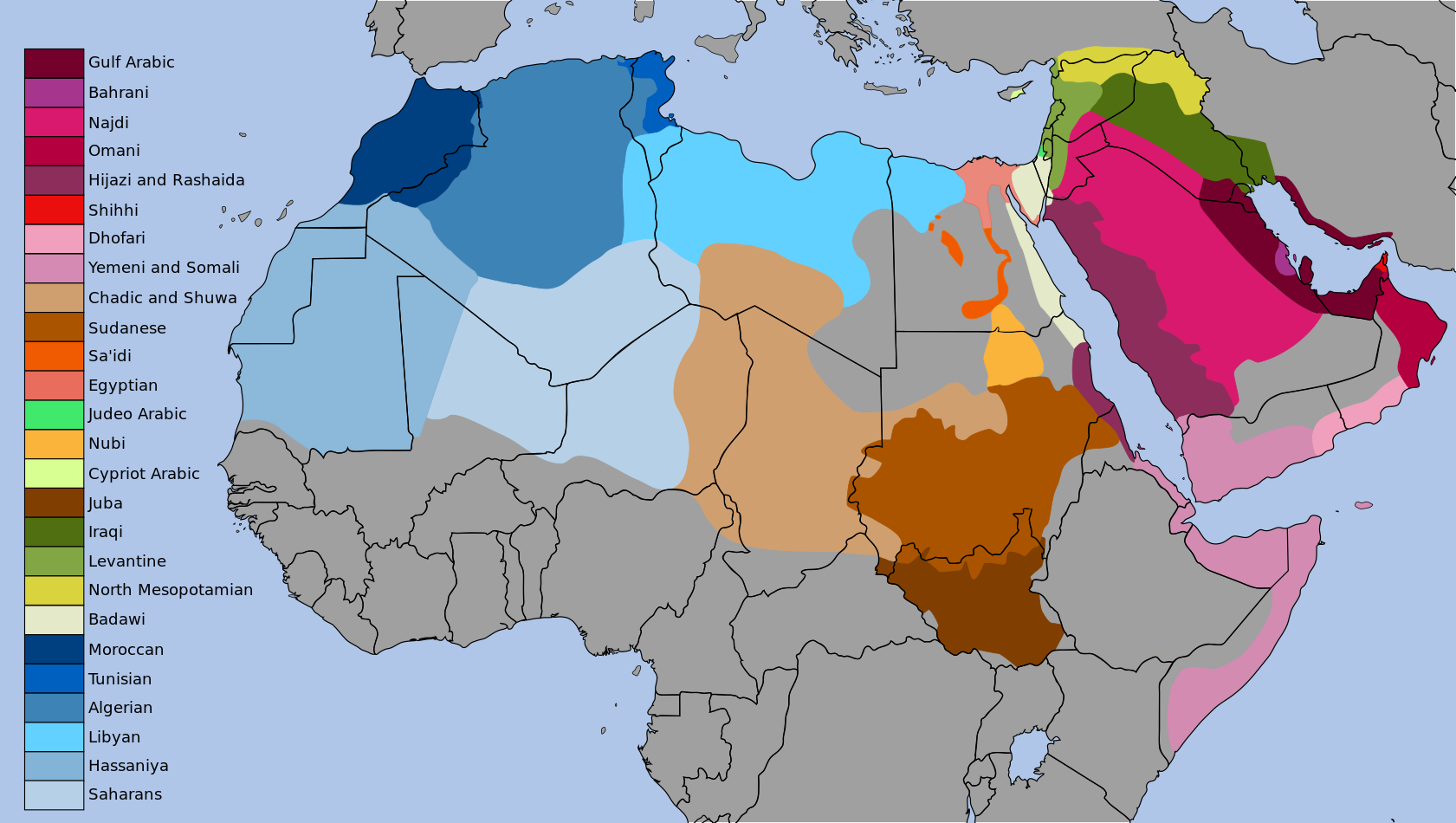
Varieties of Arabic
Quick Links * Spotlights
- The Best 100 Arabic Books (According to the Arab Writers Union)
- What are considered the greatest works/writers of Arabic
- Aranib: Arab Writers in English
- Translators Recommend Arab Authors to American Book Publishers
- 10 Books By Arab Women Writers That Should Be Translated
- 100 Recommended Books by Arab Women for Your 2017
- 20 Books to Read for Arab American Heritage Month
- 13 of the Most Influential Arab Female Authors
- 10 modern Arab writers who are proving that Arabic still matters
- 5 Powerful, Magical Books by Contemporary Female Arab Writers
- Top 7 Books by Moroccan Writers
- 9 Essential Books by Arab Writers - Publishers Weekly
- 10 Remarkable Women in Arab American Prose
- Classics of Arabic Literature | Five Books Expert Recommendations
- Mumtaz! Eight Arabic Literary Standouts All Book-Lovers Should Know
- Arabic Literature (in English) This blog publishes daily posts in English about a wide variety of topics from the Arabic literary scene, including, but not limited to, translation, author interviews, awards, publishing, freedom of speech.
- 22 Arab Authors on Their Favorite Reads of 2017 – ArabLit
- Arab Women Writers
- Famous Lebanese Authors | List of Popular Writers From Lebanon
- Out of the margins: Arabic literature in English - Asian and African
- The Radius of Arab American Writers | Poets & Writers
ديوان العرب / منبر حر للفكر والثقافة والأدب
-
Advanced Arabic Literary Reader by
ISBN: 9781317572909Publication Date: 2016-08-05Advanced Arabic Literary Reader is a truly representative collection of literary extracts from across the Arabic-speaking world. Extracts from each country in the Arab world have been carefully selected, with a balance of both male and female writers and prominent and emerging voices, providing a unique window into the Arab world. Suitable for both class use and independent study, each extract is supported by an introduction to the author, pre-reading activities, comprehension questions and discussion questions. These activities are designed to help learners expand and reinforce their vocabulary, develop their oral and written proficiency and stimulate further exploration of the cultural and historical background of the texts. Written entirely in Arabic, the Advanced Arabic Literary Reader is an essential text for advanced students who wish to further their reading, speaking, and writing ability in Modern Standard Arabic. Free audio recordings of the extracts are available online at www.routledge.com/books/details/9781138828698/ to enable students to improve listening skills. -
The Arabic Writing Tradition, an Historical Survey, Volume 1 by Professor Dr Fuat Sezgin meticulously documented the scientific writings and advances achieved by Muslim scholars. His renowned Geschichte des arabischen Schrifttums(GAS), the largest bio-bibliography for the Arabic literary tradition in general, and the history of science and technology in the Islamic world in particular, is still of utmost importance for the field. The Arabic Writing Traditionoffers English translations of volumes 1-9, and includes information about renowned figures (writers, poets, philosophers, physicians, scientists, linguists etc.) from the Islamic world in the following subjects:* Qurʾānic studies, law, mysticism (vol. 1)* poetry in Arabic until the eleventh century CE (vol. 2)* the history of Islamic medicine (vol. 3)* chemistry (vol. 4)* mathematics (vol. 5)* astronomy (vol. 6)* astrology (vol. 7)* lexicography (vol. 8)* grammar (vol. 9)
ISBN: 9789004522688Publication Date: 2022-12-22
Middle East & Islamic Studies Curator

Cornell University
Ithaca, NY, 14853
USA
ah16@cornell.edu